Rasterization
- 前两点算是上一节光栅化的内容
Painter’s Algorithm
- 从远到近画,把深度排序(O(nlogn)),然后画出来
Z-Buffer
每个像素永远去记录这个像素所表示的几何最浅的深度
z目前设置为总为正的,意为与相机的距离
生成最终渲染图的同时,还需要另一个图像,储存像素所看到的最浅的深度信息(深度图/深度缓存)
Z-Buffer Algorithm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
//初始化深度缓冲为正无穷 //在光栅化过程中: for(each triangle T) { for(each sample(x,y,z)in T) { if(z<zbuffer[x,y])//目前最近的采样点 { framebuffer[x,y]=rgb;//更新颜色 zbuffer[x,y]=z;//跟新深度图中该像素的深度 } } }
复杂度:O(n)(n个三角形*常数个像素个数)
由于深度是浮点型,而浮点型的相等是很困难的,基本上是不会一样的,但也是有出现的可能,但在本课不做讨论
不是对每个像素做z-buffer而是每个采样点(比如MSAA)
这是一个非常重要的算法,应用在所有的GPU上
Shading(着色)
- 对一个物体应用一个材质
- 一个简单的着色模型:Blinn-Phong Reflectance Model
- 镜面高光(Specular highlights)、漫反射(Diffuse reflection)、环境光照(Ambient lighting)
Shading is Local(着色具有局部性,不管阴影)
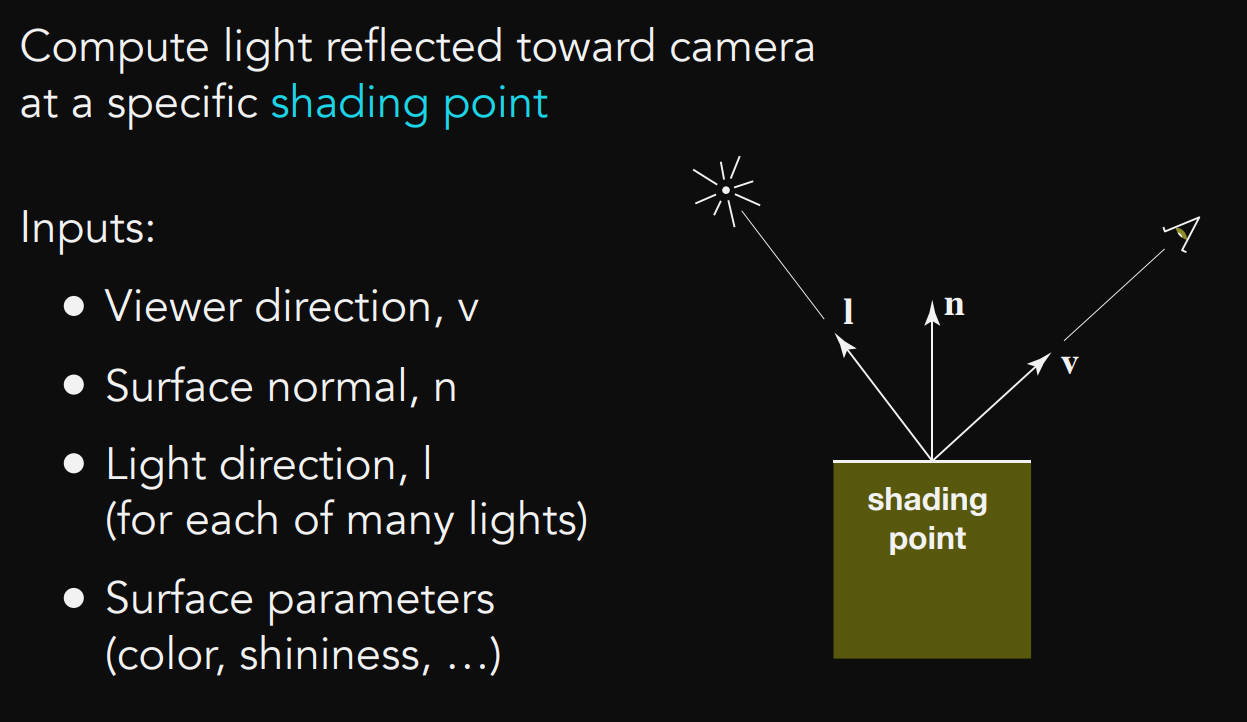
先定义一些变量,每一个shading point都有以下inputs(方向都是单位向量)
注视方向,v
表面法线,n
光照方向,l
表面参数,颜色、亮度
着色具有局部性,并不会生成阴影
Diffuse Reflection
反射到四面八方
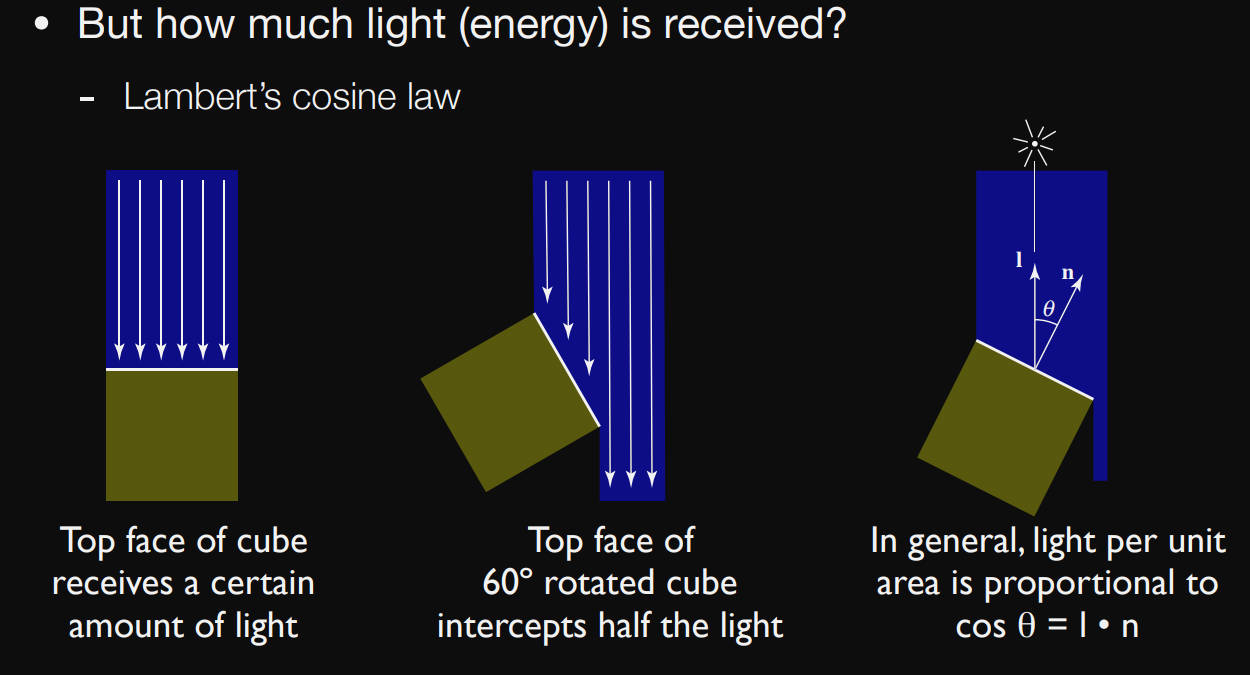
Lambert’s cosine law(光线与发现的夹角的余弦):$\cos\theta = \vec{l}*\vec{n}$
shading point处接收到的光照能量与cosθ成正比
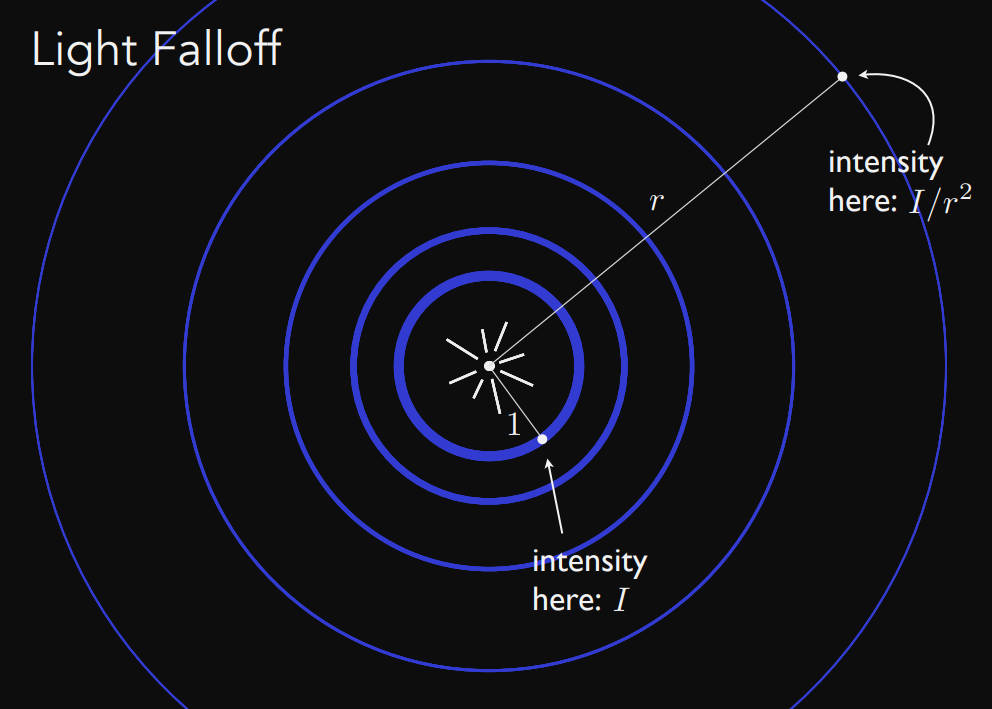
- 点光源的光线传播的能量衰减与距离半径r^2成反比
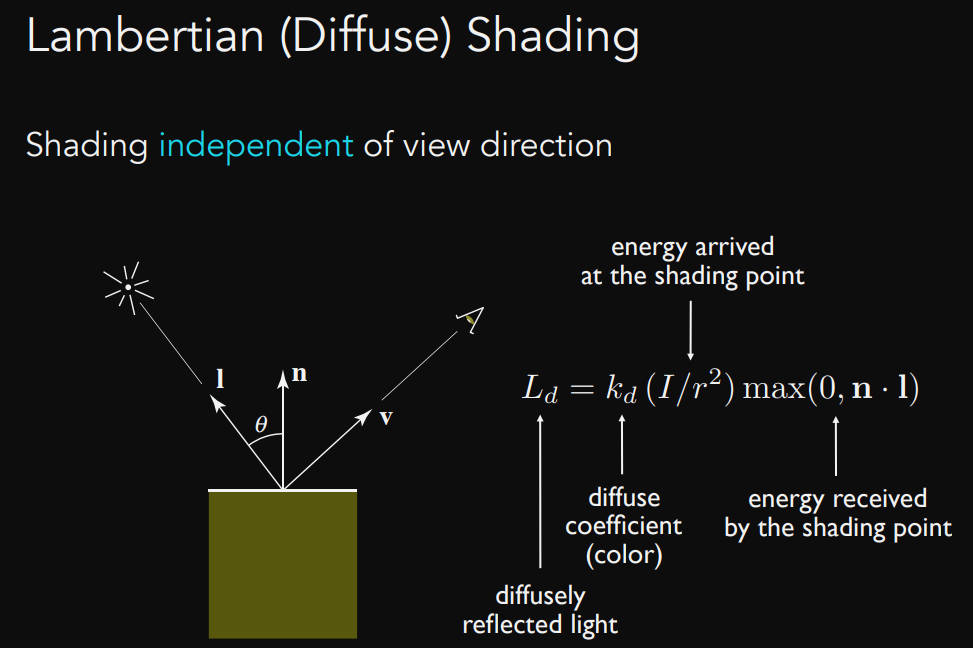
$k_d$是漫反射系数(颜色吸收,1意味着不吸收能量,全部反射出去,0意味着全吸收,表现为黑色;如果是一个向量,就可以表示颜色了,其实就可以是rgb),$I/r^2$是光线到达着色点处的能量大小
\[L_d = k_d(I/r^2)max(0, \vec{n}\cdot\vec{l})\]当光线方向和法线方向夹角大于90°时不考虑这个光,此时$\vec{l}*\vec{n}<0$,因此取0
无论从哪个方向看,同一个着色点的亮度是一样的
作业2
任务描述:
创建三角形的 2 维 bounding box。
遍历此 bounding box 内的所有像素(使用其整数索引)。然后,使用像素中
心的屏幕空间坐标来检查中心点是否在三角形内。
- 如果在内部,则将其位置处的插值深度值 (interpolated depth value) 与深度
缓冲区 (depth buffer) 中的相应值进行比较。
- 如果当前点更靠近相机,请设置像素颜色并更新深度缓冲区 (depth buffer)。
创建bounding box其实就是取三角形三个点的最小x值作为box左上角的x坐标,三个点的最大y值作为box左上角的y坐标,三个点的最大x值作为box右下角的x坐标,三个点的最小y值作为box右下角的y坐标
检查是否在三角形内,就是利用
insideTriangle函数来判断,通过判断向量叉乘的z的正负来确定点是否在三角形内。已知Q点和三角形$P_0P_1P_2$,分成三个向量:$\vec{P_0P_1}、\vec{P_1P_2}、\vec{P_2P_0}$,分别和$\vec{P_0Q}、\vec{P_1Q}、\vec{P_2Q}$做叉积,如果得到的向量方向一致,说明点Q在三条边的同侧(如都在边的左侧),那么就在三角形内,否则(一旦出现叉积结果方向不一致),就说明在三角形外。深度插值算法给了,但注意要取个负号才能变正
使用set_pixel函数来设置像素
源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
static bool insideTriangle(int x, int y, const Vector3f* _v)
{
// TODO : Implement this function to check if the point (x, y) is inside the triangle represented by _v[0], _v[1], _v[2]
Eigen::Vector3f p0p1(_v[1].x() - _v[0].x(), _v[1].y() - _v[0].y(), 0);
Eigen::Vector3f p1p2(_v[2].x() - _v[1].x(), _v[2].y() - _v[1].y(), 0);
Eigen::Vector3f p2p0(_v[0].x() - _v[2].x(), _v[0].y() - _v[2].y(), 0);
Eigen::Vector3f p0Q(x - _v[0].x(), y - _v[0].y(), 0);
Eigen::Vector3f p1Q(x - _v[1].x(), y - _v[1].y(), 0);
Eigen::Vector3f p2Q(x - _v[2].x(), y - _v[2].y(), 0);
if (p0p1.cross(p0Q).z() < 0 || p1p2.cross(p1Q).z() < 0 || p2p0.cross(p2Q).z() < 0)
{
return false;
}
else return true;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
void rst::rasterizer::rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t) {
auto v = t.toVector4();
float alpha, beta, gamma;
// TODO : Find out the bounding box of current triangle.
// iterate through the pixel and find if the current pixel is inside the triangle
Eigen::Vector2f leftTop(floor(std::min(std::min(v[0].x(), v[1].x()), v[2].x())),ceil(std::max(std::max(v[0].y(), v[1].y()), v[2].y())));
Eigen::Vector2f rightBottom(ceil(std::max(std::max(v[0].x(), v[1].x()), v[2].x())), floor(std::min(std::min(v[0].y(), v[1].y()), v[2].y())));
for (float i = leftTop.x(); i <= rightBottom.x(); i++)
{
for (float j = rightBottom.y(); j <= leftTop.y(); j++)
{
if (insideTriangle(i, j, t.v))
{
std::tie(alpha, beta, gamma) = computeBarycentric2D(i+0.5, j+0.5, t.v);
float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
if (-z_interpolated < depth_buf[get_index(i, j)])
{
set_pixel({ i,j,1 }, t.getColor());
depth_buf[get_index(i, j)] = -z_interpolated;
}
}
}
}
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
//auto[alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
//float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
//float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
//z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
// TODO : set the current pixel (use the set_pixel function) to the color of the triangle (use getColor function) if it should be painted.
}
- MSAA超采样反走样:就是把一个像素分为四块,检查四个小块是否在三角形内,根据个数比例修改颜色大小的比例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
void rst::rasterizer::rasterize_triangle(const Triangle& t) {
auto v = t.toVector4();
float alpha, beta, gamma;
// TODO : Find out the bounding box of current triangle.
// iterate through the pixel and find if the current pixel is inside the triangle
Eigen::Vector2f leftTop(floor(std::min(std::min(v[0].x(), v[1].x()), v[2].x())),ceil(std::max(std::max(v[0].y(), v[1].y()), v[2].y())));
Eigen::Vector2f rightBottom(ceil(std::max(std::max(v[0].x(), v[1].x()), v[2].x())), floor(std::min(std::min(v[0].y(), v[1].y()), v[2].y())));
Eigen::Vector2f pos[4] =
{
{0.25,0.25},
{0.25,0.75},
{0.75,0.25},
{0.75,0.75}
};
for (float i = leftTop.x(); i <= rightBottom.x(); i++)
{
for (float j = rightBottom.y(); j <= leftTop.y(); j++)
{
int cnt = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
if (insideTriangle(i + pos[k][0], j + pos[k][1], t.v)) cnt++;
}
if (cnt)
{
std::tie(alpha, beta, gamma) = computeBarycentric2D(i+0.5, j+0.5, t.v);
float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
if (-z_interpolated < depth_buf[get_index(i, j)])
{
set_pixel({ i,j,1 }, t.getColor() * cnt / 4);
depth_buf[get_index(i, j)] = -z_interpolated;
}
}
}
}
// If so, use the following code to get the interpolated z value.
//auto[alpha, beta, gamma] = computeBarycentric2D(x, y, t.v);
//float w_reciprocal = 1.0/(alpha / v[0].w() + beta / v[1].w() + gamma / v[2].w());
//float z_interpolated = alpha * v[0].z() / v[0].w() + beta * v[1].z() / v[1].w() + gamma * v[2].z() / v[2].w();
//z_interpolated *= w_reciprocal;
// TODO : set the current pixel (use the set_pixel function) to the color of the triangle (use getColor function) if it should be painted.
}
注意:
开始自己写的时候,只写了个判断是否在三角形内的函数,开始想用叉乘出来的向量进行判断,但标准化可能出问题了(我直接用的Identity()函数),导致绘制出来的是矩形,怪。后来改成用z值得正负来判断就行了
光栅器自带得
depth_buf数组其实就是深度缓冲区,并且使用get_index()函数可以通过坐标映射到缓冲区中的位置在算bounding box的时候注意向下取整和向上取整,不然绘制的那个小三角形会很奇怪
在遍历bounding box的时候,用的是float变量
要把main.cpp文件中
get_projection_matrix函数的t值加个负号,才能显示正的三角形(t也就是摄像机的向上方向)上面其实也不一定需要给t加负号,在设置投影矩阵的时候,zNear和zFar都加个负号也行
又写了一遍,但大体上差不多,就不再记录了